If a pneumatic cylinder is present on your next project or application, here’s an in-depth and detailed explanation of its functionalities, features, and uses. Check out the article to learn more about them and how they work in various applications.
What is a Pneumatic Cylinder?
Once you start studying or looking through various industrial machines and automatic equipment used in construction sites, manufacturing companies, and commercial devices, you will begin to learn about the Pneumatic Cylinder. It is the device used in mechanical and industrial processing operations through the medium of pressurized air as its source of energy and force. One of the primary purposes of this is to move, lift, pick, or eject specific objects that might require a higher level of force to work. Additionally, it makes a linear motion of force and strength with a quiet and cost-efficient operation.
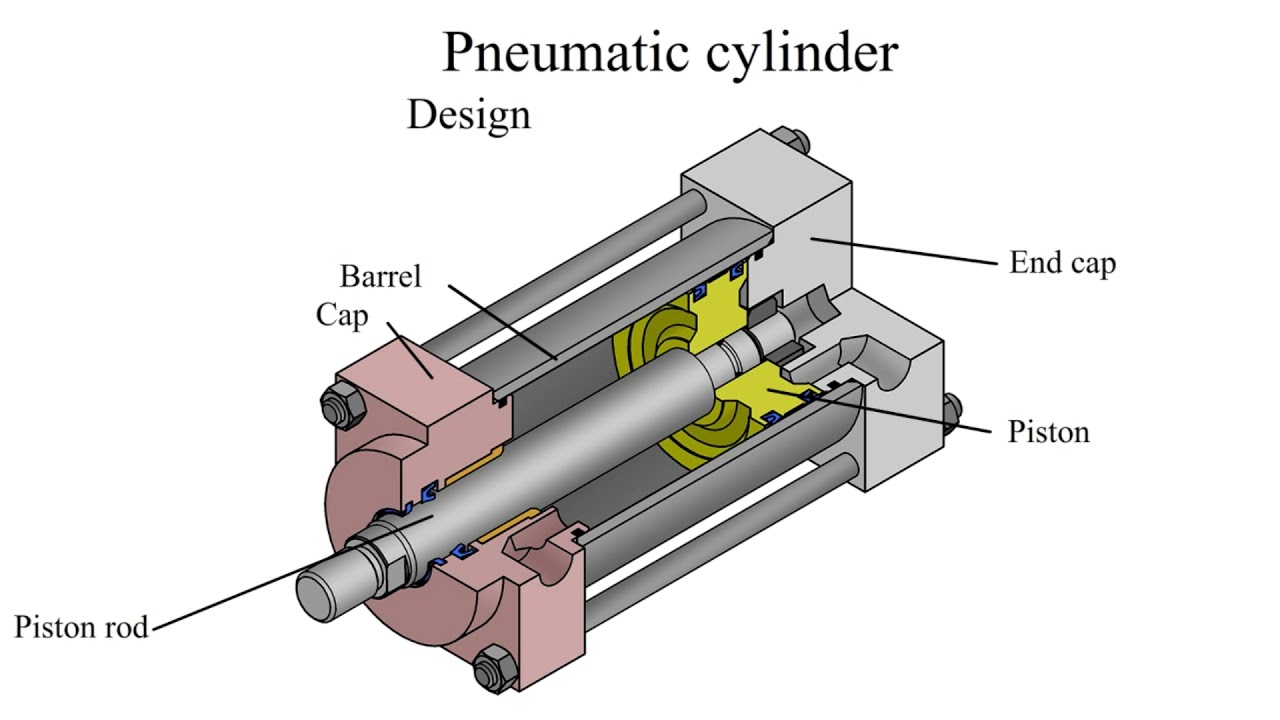
Pneumatic Cylinder Parts and Functions
For every piece of equipment or tool to work, it is composed of different components with specific functionalities working together to provide better performance. And its general purpose could only happen with the help of its parts and their functions. Here’s a detailed review of them:
1.The Bore
The cylinder will need protection for its components for a more efficient and reliable performance, and the bore does this role with the front-end and rear-end caps for protection when the actuation starts.
2.The Piston
The piston inside is described as a disc. It is one of the most vital parts, and its primary purpose is to provide the division between the chambers. Also, it is movable and can go back and forth in a linear motion.
3.The Piston Rod
Based on its name, it is also a part of the piston, and both must have a connection with some components of the machine. The role of the piston rod is to provide the stroke of push and pull.
4.The Piston Cushioning
The general purpose of the piston cushioning is to make sure that there is less impact when the actuation starts. It mainly works closely on the vibration and noise during the operation and lets the piston move faster.
5.The Tie Rods
The presence of tie rods is also very critical since it contributes for protection against shock. This type of rod is threaded steel that runs around the cylinder, plus the average size used depends on the level of force that the cylinder produces.
Pneumatic Cylinder Working Principle
The general purpose of this is to give support through force and strength by using pressurized air, and the main working principle depends on the two main classifications. Here’s a quick explanation of each of them:
1.Single-Acting
This only makes a motion in one direction, like going back and forth. The pressurized air pushes the piston to work in a linear motion, along with the mechanical springs.
2.Double-Acting
This type controls the piston’s motions and works in both directions. The only downside of double-acting is that it consumes more energy and does a complicated operation that is unsuitable for applications needing a cylinder to remain in a particular position. Additionally, it has more stroke length and force.
5 Types of Pneumatic Cylinder
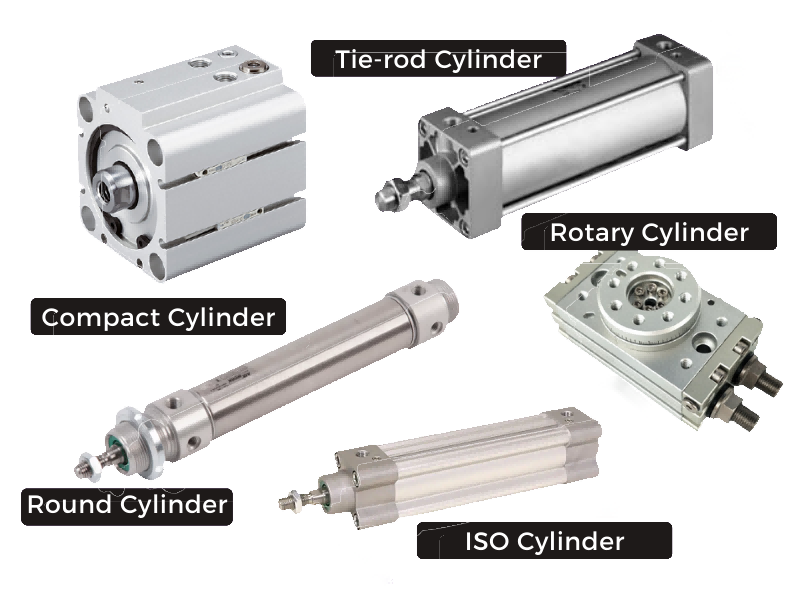
Here are the other types used in different applications:
1.Rotary Cylinders
This one operates by converting the pressurized air into an output called torque. Aside from this detail, the direction of this cylinder during the actuation process is from clockwise to counterclockwise.
2.Rodless Cylinders
When the loads are in motion together with the piston in a straight line, the type of cylinder used is the rodless. It uses less internal pressure since the only movement is through the side of the chamber.
3.Tandem Cylinder
In this type of cylinder, there are two pistons in only one rod, and that’s the reason why it is also called a combination cylinder. It provides higher force than other cylinders because of the two double-acting cylinders connected during the actuation.
4.Telescopic Cylinder
This one uses segmented tubes and provides longer strokes since it is telescopic in detail. The working procedure begins when the pressurized air fills the cylinder, and the tubes eventually extend.
5.Welded Cylinder
This type of cylinder does not need the presence of a tie rod. The name explains everything, and it means that the end caps from the cylinder are welded, making it achieve top-notch durability and quality in compaction.
What is Pneumatic Cylinder Use For?
They are essential in most industrial machines, heavy-duty manufacturing procedures, and other devices. Here are some of its specific uses:
1.Industrial Automatic Machines
It is an excellent help for manufacturing companies in line with industrial processing that needs automatic material handling for a more efficient work environment, like clamping pieces of components, lifting objects, or pushing and pulling equipment.
2.Operational Tools
It can be present in operations requiring tools for cutting, changing, or controlling materials in a specific position and frequently moving at a higher speed for efficiency.
3.Automotive Industry
It impacts different vehicles, especially when fixing some parts by welding. Also, it provides a more efficient controlled movement towards the assembly of car components.

4.Food and Beverages Processing Industry
Since it is considered a more hygienic type of cylinder, the food processing industries take advantage of its ability to label some products and provide rapid sorting, organizing, and filling of containers during production.
5.Construction Equipment
It also functions as part of the equipment used in a construction site, specializing in providing support of force and strength to heavy-duty performances done by excavators, pumps, or cranes.
6.Aerospace Industry Equipment
It is also functional for most aerospace industry equipment, such as deployment to the cargo doors for opening and closing operations and providing control management to rudders and flaps.
7.Medical Industry Equipment
It can also be found in some medical equipment, and its role is to provide smooth and efficient control management for the movements of surgical tables, hospital beds, and other movable and lifting equipment inside a medical firm.
Conclusion
Most industries use pneumatic cylinders’ mechanism of producing force to help in different activities, such as lifting and picking objects, providing ejection and blocking, and clamping and placing objects in a particular piece of machinery during an operation.
They are impacting different processes and operations, increasing the demand for them in the market. However, specific cylinders are suitable for a particular project or application, differing in materials, durability, and designs.
In this article, the different types are highlighted, and their differences are pointed out, making it easier to determine which to purchase. Additionally, having a ground of their details can be a good advantage when planning to use them in a project or application.
FAQs:
1.Do pneumatic cylinders need oil?
Since pneumatic cylinders do not self-lubricate, most parts need oil for their internal components for periodic maintenance. Also, lubricity coming from high-quality oils will make the cylinder work better even under high pressure.
2.Which is better, pneumatic or hydraulic?
Both pneumatic and hydraulic cylinders are helpful and have different functionalities depending on the application. To get further details, you can check the critical differences between the two to understand what suits your project.
3.How is pneumatic used in everyday life?
Pneumatic is used daily through its ability to pick up and lift objects or equipment and move and place equipment in a straight motion. You can see it in most equipment nowadays, like paint sprayers, pavement breakers, and rock drills.

