A pneumatic press machine uses compressed air to create force for many industrial uses. It can stamp and shape metal by taking advantage of pressurized air rather than electricity or hydraulics. By replacing air pressure for other power sources, the machine adds flexibility to many factory processes.
Let’s explore further into pneumatic press machines and their benefits.
What is a Pneumatic Press?
Compressed air powers a pneumatic press machine, enabling it to achieve force for varied uses in industries. But what is a pneumatic press? Let’s look at the various components that make up this machine.
- Compressor – Here’s where the magic begins. The compressor pulls in air, giving it a squeeze create more pressure. This crucial part keeps the machine chock-full of compressed air for use in different industrial processes.
- Reservoir – Also known as the air receiver tank, this element stores the air freshly squeezed by the compressor. This tank is essential to guarantee a steady and dependable air flow into the system.

- Pneumatic Cylinder – It is one of the essential systems of an industrial pneumatic press. It converts the energy found in compressed air into mechanical motion. It has a cylindrical chamber and a piston located inside. Compressed air moves the piston to create a linear motion for exerting force.
- Piston – Found within the cylinder, the piston moves due to pressure shifts. This piston action provides the force behind machine’s operations. It is an integral part to any benchtop press machine.
- Control System – The press also has a control system. It’s intricate, with multiple parts to manage compressed air flow, including valves, regulators, and sensors. They handle the speed, force, and timing of operations.
- Valves – Air valves manage the course and flow of compressed air. They start and stop the pressurized air to the cylinder. Therefore, they will determine the overall force, speed and accuracy of your press machine when in use.

- Pressure Regulator – The regulator adjusts and manages air pressure in the system. This ensures a consistent force application by the machine.
- Safety Features – Every pneumatic press system has safety features to prevent accidents. These include emergency stop buttons, protective guards on moving parts, and safety interlocks.
- Tooling and Workpiece Interface – These are the molds, dies, and tools used for processing or shaping a product. The workpiece interface refers to where the material is processed.
Knowing each component of this machine is essential for proper operation, maintenance, and safety. When there is a malfunction, you must inspect each of these components to ensure proper replacement.
How Does A Pneumatic Press Work?
Simply put, the machine uses compressed air to create force and motion. Let’s look at a step-by-step of a pneumatic press working principle.
Supply and Distribution of Compressed Air
The machine relies on compressed air to work. An air compressor is responsible for supplying compressed air to the system. It gathers atmospheric air and then compresses it in a tank. The air is distributed in a network of pipes and valves till it reaches the machine.
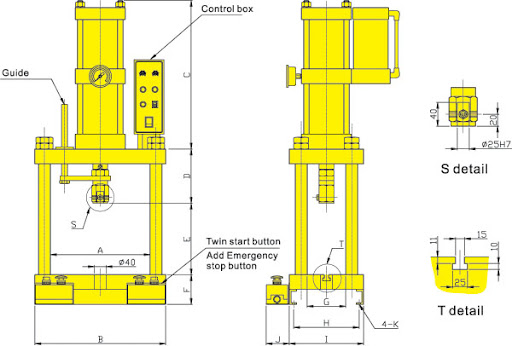
Force Generation
The industrial pneumatic press has pneumatic cylinders that convert the compressed air into mechanical motion. The pneumatic cylinder has a piston that moves when compressed air is introduced. When the piston moves, it creates force.
The force coming from the pneumatic cylinder may be adjusted accordingly. This is possible through regulating air pressure or controlling the size of the cylinder.
Pneumatic Press Action and Release of Compressed Air
The force created in the pneumatic cylinder is then transferred to a tool or the workpiece being processed. It happens through a plunger or ram connected to the piston. Every pneumatic press system has a control system.
As such, you can control the force, speed, and duration during the pressing process. The control system includes pressure regulators and valves. Once the process is completed, the control system releases the compressed air from the cylinder. The piston returns to its previous position in readiness for the next cycle.
Pneumatic Press vs Hydraulic Press
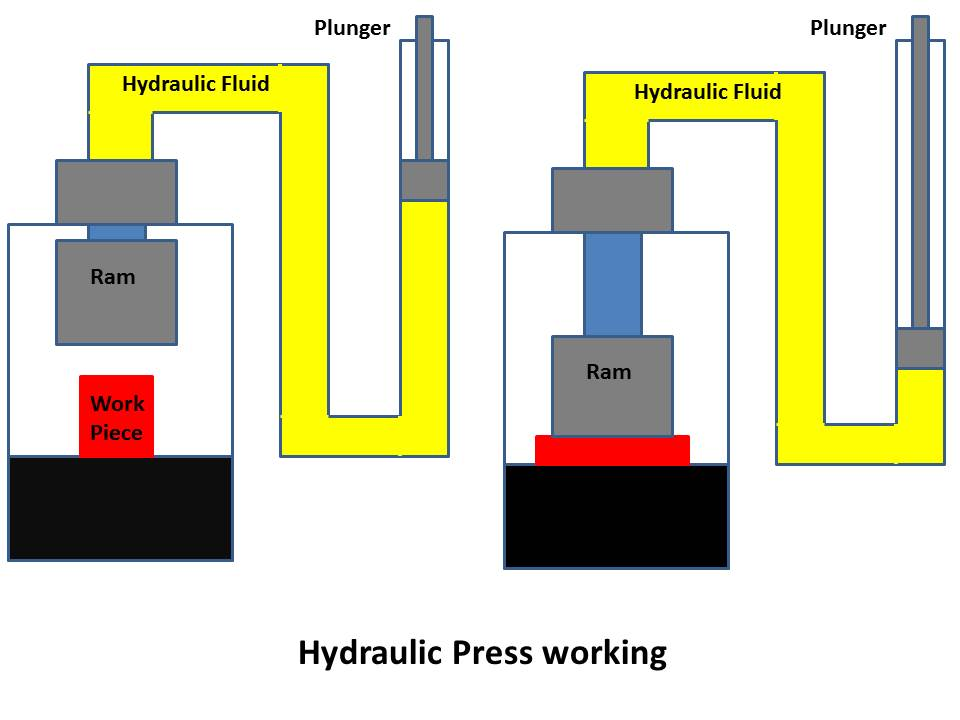
Compressed air and liquid presses are utilized wide range of applications requiring the exertion of pressure. They are employed for shaping substances, imprinting, and molding procedures. While their functions are similar, there are some notable differences.
Let’s look at the stark differences between pneumatic and hydraulic presses.
- They utilize different power sources. A pneumatic press uses compressed air to function, relying on the force created by air under pressure. Meanwhile, a hydraulic press depends on hydraulic fluid, generally oil, as its power.
- A pneumatic press operates using compressed air that moves through a piston. In contrast, a hydraulic machine press generates forces by passing hydraulic fluid within a hydraulic cylinder and piston. Both press types function through the movement of a piston. However, they differ in the medium used – air versus liquid – to exert pushing or pulling force.
- Air-powered presses produce less pressure than liquid-powered presses. For this reason, they are utilized in tasks that do not require much force with quicker cycles. Liquid-powered presses generate more pressure and are employed in metal shaping or heavy-duty pressing jobs requiring additional force.

- Pneumatic press machines react more rapidly than hydraulic presses due to their brief cycles. They are generally applied in situations requiring significant velocity. Hydraulic presses are slower and employed in contexts where swiftness is inconsequential.
- An air-powered press delivers the finest precision and control. It’s ideal for tasks requiring exact and reproducible outcomes. A fluid-driven press offers exact oversight of force and placement. These are used in a wide range high-precision applications, for example, developing elaborate shapes.
- Small pneumatic presses are well-suited for lighter tasks. They can mold plastics, shape some metals, and aid basic assembly work. However, heavier jobs requiring significant force call for hydraulic presses. These industrial machines are used for metal shaping techniques like forging and deep drawing. Whether pneumatic or hydraulic, the appropriate press helps transform raw materials into finished products by applying compressed air or liquid pressure.

- The pneumatic press requires less upkeep than the hydraulic press. Its structure is more straightforward, with fewer parts. Hydraulic presses demand more maintenance due to their intricate design. For example, the hydraulic fluid levels and seals need periodic inspections to ensure proper functioning.
When selecting a press machine, you need to look at the job, the necessary force, and speed. Additionally, think about the materials being worked on. Pneumatic presses are well-suited for lighter duties, whereas hydraulic presses handle heavy-lifting jobs.
Advantages of a Pneumatic Press
When considering machines for industrial uses, benchtop pneumatic presses offer various benefits. The following are some key advantages to investing in this machine.
Precision Control
An air-powered press allows for exact control over the applied pressure. It’s ideal for jobs requiring precise and consistent outcomes. It sees primary use in assembly applications demanding accurate force.
Reduced Noise Levels
Industrial pneumatic presses offer a quieter alternative to other press types. They function more soundly, cultivating a comfortable and hushed work environment. This characteristic makes them highly beneficial in situations where noise levels need minimization.

Increased Safety
An industrial pneumatic press contains built-in safety features to make sure the entire process is secure. For example, it has overload protection and emergency stop mechanisms. You will be more protected when using the machine and they also enhance safety in the workplace.
Ease of Automation
Robotics work well with pneumatic presses. They can also link easily with other machine-led production steps. This makes the workflow smooth and supports reliable, high-volume output. If you are running any industrial process with an air-powered press, you can count on ease of automation and improved productivity.
Low Maintenance Costs
A pneumatic press has less parts than a hydraulic press. That means it needs less upkeep. So, you will save on maintenance costs and needs. It also minimizes downtime and overall upkeep expenses. You may reallocate these funds for other processes.
Environmental Considerations
Air-powered presses are friendlier to the earth than liquid-run presses. They don’t operate with hydraulic fluids and pose no environmental risks. They’re ideal for industrial settings aiming for sustainability and respecting environmental laws.
Temperature Sensitivity
Pneumatic presses work well in any temperature, unlike others. They provide consistent results in changing climates without problems. So, temperature changes won’t affect your productivity or output.
Easy Customization Options
An industrial pneumatic press can be customized to meet your production needs. It can change and function well across various industries. The machine is effective in electronics, automotive, and packaging industries.
Effortless Installation
Benchtop pneumatic presses are simpler than hydraulic ones. They’re lighter and quicker to set up. They fit right into assembly lines.
Global Availability
People use industrial pneumatic presses all over the world. Therefore, getting replacement parts, repairs, or maintenance done is fast and efficient.

Conclusion
Pneumatic presses are flexible. They use compressed air to give you exact control in many tasks. The machine is steady, dealing with all sorts of stuff for top-notch productivity. These systems are great for plastic and metal industries.
Whether you are compressing polymers, shaping alloys, you name it, they’re ready. They are dependable, changeable, user-friendly. Pneumatic presses are a win for modern manufacturing. They smooth out the process and jack up productivity across the board.

