The pneumatic valve is one of the most important components of air-operated systems. It houses ports that allow the controlled passage of air, and can be manual or electrically-operated. To provide you with a better understanding of this type of product, we compiled this guide to explain it in detail. This is what you will learn at a glance;
- What a pneumatic is
- How it works and its function
- The different types of the valve, and
- Its common applications
What is a Pneumatic Valve?
A pneumatic valve is a type of airflow control device used in pneumatic systems. Pneumatic systems rely on the pressure of compressed—or other type of gas—to do work, usually by causing a movement.
Depending on the required action, the pneumatic control valve can be designed with two or more ports. To control the ports’ opening and closing, it may use a manual or automated mechanism called a solenoid.
A pneumatic valve can also mean a type of valve that’s actuated by air and used with any medium, including liquids. In this article, however, we will concern ourselves with the first meaning of the device, which is the type that pneumatic systems use to regulate the flow of pressurized gas.
Pneumatic Valve Specification
Pneumatic valves are important devices that must be designed and built to various specifications. Before proceeding, therefore, it’s essential that we learn about these specifications. They include the following;
- Pressure Range: this is the range of pressures that the valve is designed to handle, and usually expressed in Psi, PA or Bars
- Response Time: this pneumatic valve specification indicates the time that the valve takes to switch from one state to another after being actuated
- Flow Capacity: the valves capacity in regard to the amount of air that can flow through it
- Port Size: the dimensional measurements of the valves ports
- Cycle Rate: the highest number of cycles that the valve can achieve within a specified amount of time
- Coil Voltage: this applies to electrically-actuated pneumatic valves. It specifies the maximum voltage that the actuation coil can handle
Resource: https://www.mdpi.com
How Do Pneumatic Valves Work?
Pneumatic valves work by taking in compressed air, directing it through internal pathways, and then allowing it to exit via openings called working ports. From here, the air can be made to operate an actuator and perform a useful function.
To do that, it come with a means to open and close internally placed air channels in a controlled way. This is usually with the use of a spool that can move back and forth, either manually or with the use of an automated mechanism.
To understand that better, let’s take a look at the parts that make up a typical pneumatic valve assembly. After that, we’ll see how it works using the various components that it’s composed of.
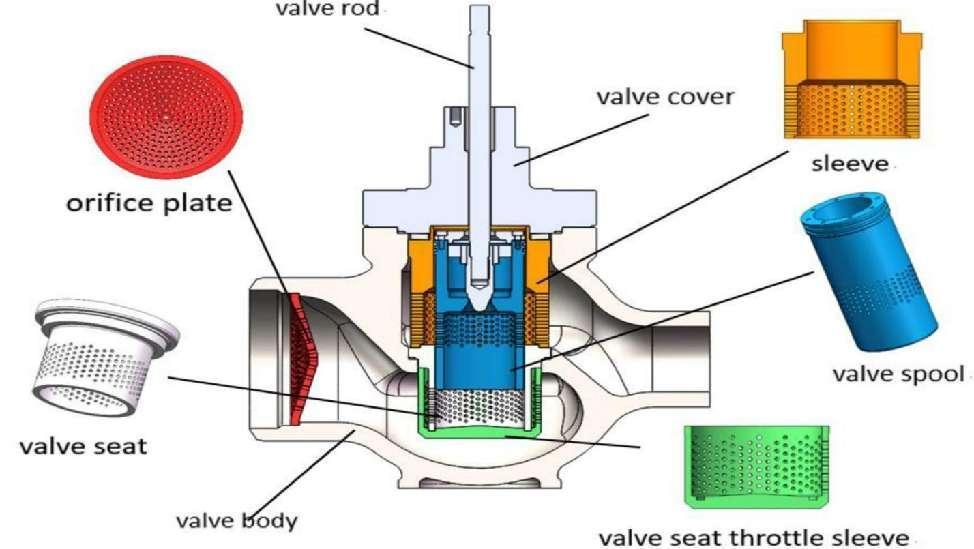
Air Valve Parts
A pneumatic valve is made up of these main parts: the body, inlets and outlets, an array of internal pathways called ports, a moving element to open and close the ports called a spool, and—if electrically operated—a solenoid mechanism to move the spool.
Air Valve Operation
The pneumatic valve working process is typically based on the movement of a spool. When inactivated, the spool is held stationary on one side of the valve. Upon activation, air under pressure flows into the valve and then this happens:
- The spool moves to open and close the necessary ports.
- The spool contains raise parts called glands and recessed sections called grooves.
- These align with the ports to direct compressed air through the required pathways and out through the exit ports.
- That way, the air can reach the actuator to generate mechanical movement and do some work.
- After the air has moved an actuator, it goes through an exhaust circuit so it can be safely released into the surrounding space.
- In one of the most common types of the valve called a pneumatic solenoid valve, a PLC module controls the spool movement using an electromagnet.
- This allows for precise and automated opening and closing of the ports.

Resource: https://www.youtube.com/watch?V1iyfuqmUhE
Pneumatic Control Valve Function
The function of pneumatic valve systems is to direct air as required and operate an actuator. The actuator then does helpful work, such as moving a load or automating an industrial process. Most commonly used in industrial equipment and systems or power tools.
Ideally, the valve receives compressed air from the source and, using a series of ports and a moving part called a spool, channels air to the working ports or outlets as required. This helps to ensure a controlled flow.
In order to perform its function, the valve is connected to the air source at one end. This is typically a compressor and air preparation unit. On the other end, the valve is connected to an actuating mechanism, which is often a moving piston inside a cylinder.

Resource: https://www.youtube.com/watch?V1iyfuqmUhE
Types of Pneumatic Valves
Different types of pneumatic valves are available for different kinds of applications. Generally, the valves are categorized based on the number of ports, switching positions, actuation or opening and closing mechanisms, and whether they stay open or closed when not activated. Most commonly, these valves are classified as:
2-Way Pneumatic Valve
This is the most basic type of pneumatic valve, consisting of one air entry port and one exit port. In the closed state, they do not allow any air through. When opened, two-way valves allow air in through the inlet port and out via the exit port and into the actuator.
3-Way Pneumatic Valve
Just as its name indicates, the 3-way valve comprises three different ports. Each port has a specific function. One connects to the airflow, allowing pressurized air, while another connects to the actuator. The third port, on the other hand, acts as the exhaust.
4-Way Pneumatic Valve
The 4-way pneumatic valve comes with four different ports. One port connects to the airline, while two ports are linked with the actuator or actuators to operate their opening and closing. The fourth port then acts as the exhaust opening.
The four-way pneumatic valve is one of the most popular. It allows for reversed cylinder movements or a back-and-forth motion, which many systems, devices, or equipment require.
Sometimes, this valve comes with a fifth port included. The additional port is usually a pressurized air path to supplement the existing pathway and allow for two different pressures to be used.
Spring Offset Pneumatic Valves
These are named so based on the method used to switch them and direct the flow of air. They use a spring mechanism to return to their former state and position after they have been actuated. The spring connects to the spool, which is the movable piece inside the valve that regulates the opening and closing of the valves.

Resource: https://www.newequipment.com
Pneumatic Valve Applications
Pneumatic valve applications are wide and varied, covering a broad range of industries. You can use the device in virtually any setting, especially since pneumatic mechanisms easy to use, lightweight, and fast-acting. In additionally, you can use them in settings that are prone to sparks.
Common applications include the actuators of industrial or manufacturing systems and a variety of other uses. For example, it can be a pneumatic valve for water systems, a valve to hold or move a product during production, or a valve for a power tool.
Conclusion
The pneumatic valve is a critical component of air-operated systems. It comes with ports to regulate the flow of air or other gas which, in turn, allows it to control the operation of actuator mechanisms such as pneumatic cylinders. Different types of the valves are also available for different types of applications and other operational requirements.

