
Resource: https://forum.fritzing.org
In order to electrically control pneumatics, a special type of valve called pneumatic solenoid valve is used. This valve forms a crucial part of automated systems and remotely-operated mechanisms, providing benefits that range from efficiency to safety and convenience. Learn all about this device below, including how it works and its different types.
What is a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve?
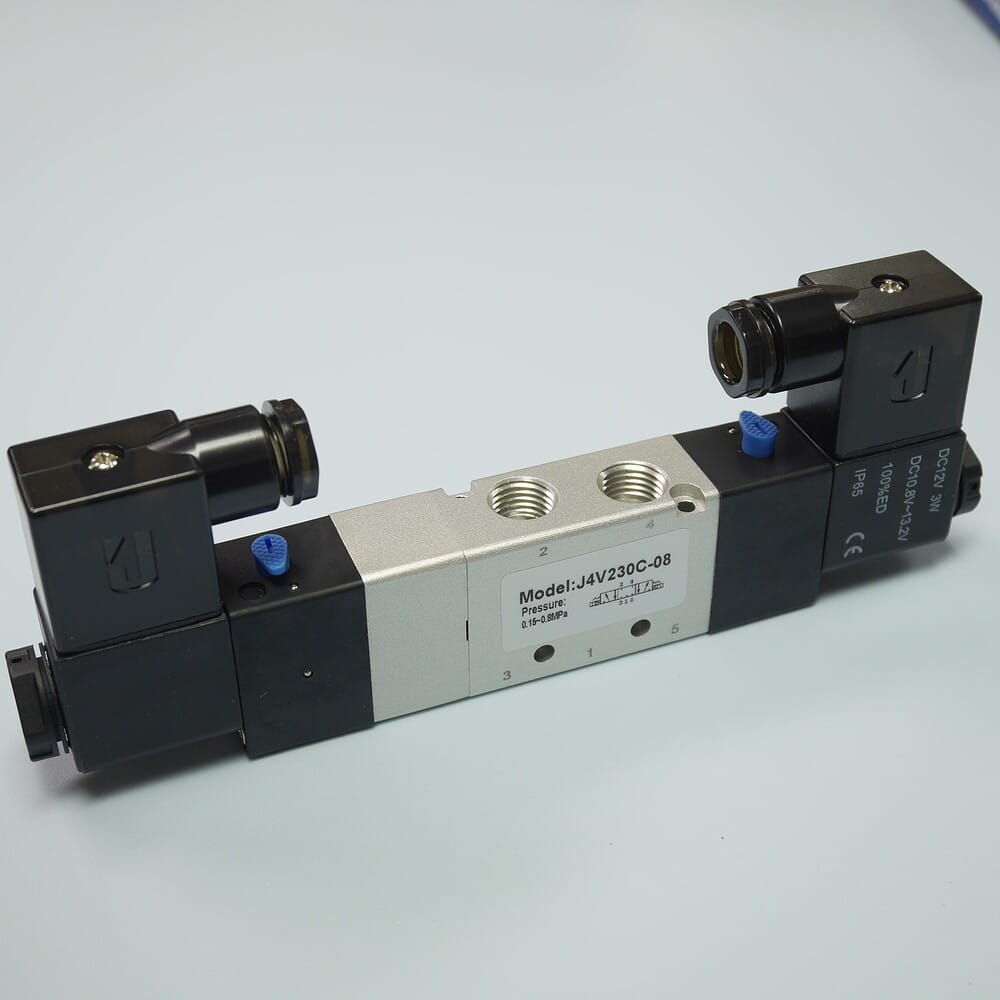
With reference to its reliance on an electromagnet to work, the pneumatic solenoid valve is a type of electrically-actuated valve used in air-operated systems. It comes with a solenoid or two attached to its body and supplied with wire terminal to connect it to a power supply.
The solenoid acts as the valve’s control mechanism, moving a plunger to open and close the valve port or ports. Different versions of the solenoid valve for pneumatic actuator mechanisms are available.
Mostly, these valves are classified by the number of ports, with the most common design being the two-port valve. The pneumatic solenoid actuated valve is also designed in several different sizes and other specifications, as we will see shortly.
Difference Between Solenoid and Pneumatic Valve
The pneumatic, electric solenoid valve is often confused with the general term used for valves that air-operated systems use to regulate airflow. So how are the two different?
- A solenoid valve is any type of valve that uses the force of an electromagnet to control flow in a hydraulic or pneumatic system. When used in a pneumatics, it’s invariably called a pneumatic solenoid valve.
- A pneumatic valve, on the other hand, is a collective term for the valves that air-operated systems use to control the motion of compressed air. These can be valves that are operated manually, using air, or electrically with a solenoid.
Specification
Pneumatic solenoid valve manufacturers make different versions of the product. When choosing one for an application, therefore, users must understand its various ratings must inform your choice. These include the following:
- Port size in inches or other units
- Minimum and maximum pressure rating in CFM
- Flow rate
- Operational temperature
- Rated coil voltage for AC or DC power
- IP rating
Resource: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=54ypTJA8HDc
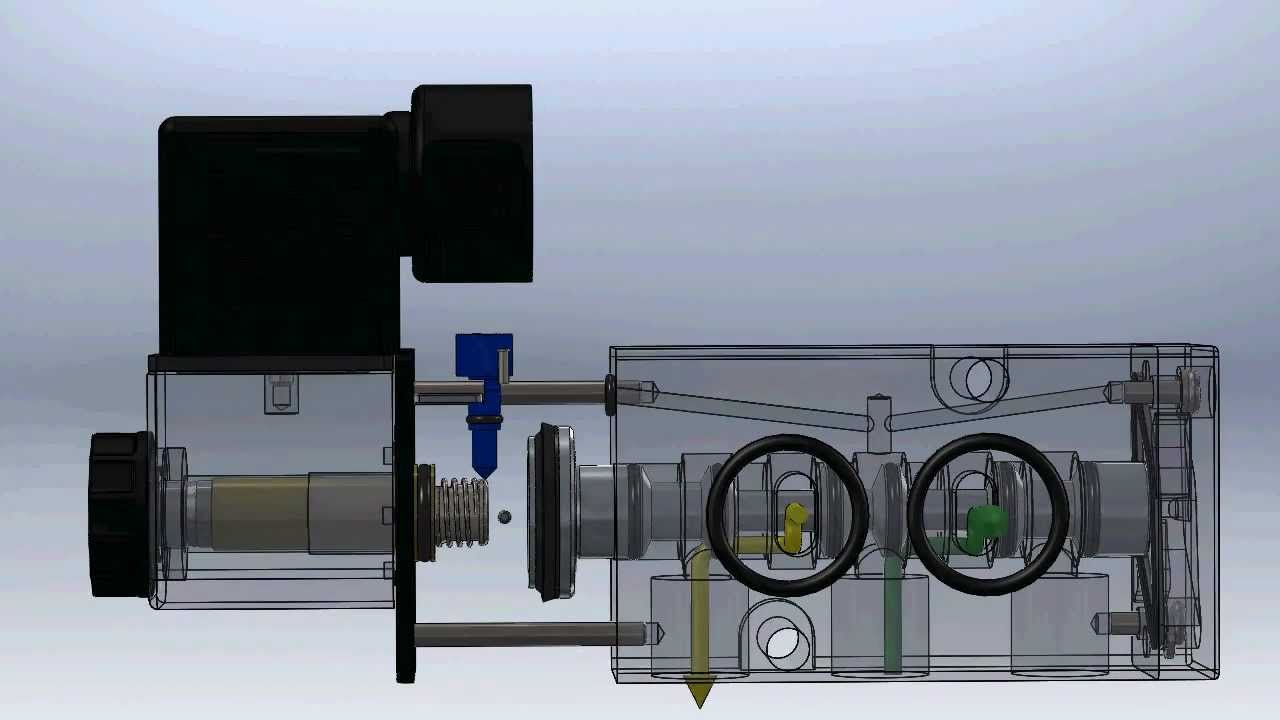
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Parts
The typical solenoid valve for pneumatic cylinder actuators or other mechanisms is divided into two distinct parts: the valve body, which is the actual valve, and the solenoid assembly, which is the electromechanical component that operates it.
Pneumatic Valve Body
The valve body is the assembly that houses the device’s internal components, including the air pathways and inlet or outlet ports. It has the inlet port that delivers air into it and exit ports that take air away to the pneumatic actuator.
Inside, the valve contains pathways that allow or block the flow of air as required. In the most common type of this valve, a spool moves back and forth. Depending on the construction, the spool may be held by a return spring or two springs on either side.
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Coil
The coil is the electrical component that, upon receiving an electric current, generates the magnetic force that the valve uses to control the flow of gas. It basically consists of these different parts: wire coil or armature, movable plunger or push and, and terminals.
The terminals supply power to the coil, while the plunger moves under the action of the coil’s magnetic field to close or open the valves port or ports. Most often, the plunger connects to a piston that pushes against the spool to move it.

Resource: https://www.youtube.com/watch?fzoCCbnz8Vg
How Does a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Work?
At the heart of the pneumatic solenoid valve operation is a magnetic coil wound around a magnetic core, or what’s called a solenoid. When supplied with an AC or DC current, the coil generates a magnetic field around the plunger. The following then happens:
- The resulting magnetic field then moves the plunger.
- The moving plunger, in turn, operates the valve mechanism to open or close it.
- Most often, the valve is a multi-port device, with the solenoid action being used to open some ports and close others.
Having looked at the pneumatic solenoid valve working principle in general, it’s worth noting that different valves of this type operate differently depending on their design and required function. In light of that, we have the following working modes.
Normally Open Vs. Normally Closed Solenoid Valve
A normally open pneumatic solenoid valve permits fluid to flow when the solenoid coil is de-energized. Activation of the coil results in valve closure. A normally closed solenoid valve operates conversely, blocking fluid flow when the solenoid coil is de-energized. When the coil is energized, the valve springs into action, allowing the fluid to flow.
Internal Vs. External Pilot Solenoid Valve
Some valves, especially those used in high-pressure systems, use both the solenoid action and line pressure to actuate, and are either internally or externally piloted. In an internally piloted solenoid valve, the fluid passing through it acts as the source of pilot signal, while an externally piloted valve uses air pressure from external source.
Single Acting vs. Double Acting Solenoid Valve
A single acting pneumatic solenoid valve only has one solenoid. When activated, the plunger moves to close or open a port or ports. When deactivated, a return spring resets it. In the double acting valve, two solenoids are placed on either side to control the valve without the need for a resetting spring.

Resource: https://www.controleng.com
Pneumatic Valve Function
The function of a pneumatic solenoid valve is to allow the electrical control of air-operated systems. This makes it an important device in many diverse applications, the most common being the controlled operation of pneumatic actuators. The electrical control of solenoid valves offers these benefits.
- Automation: a pneumatic actuator with solenoid valve can be automated with the use of hardwired logic systems or PLCs (programmable logic controllers), allowing for the intelligent control of different processes.
- Speed: using a pneumatic valve with solenoid actuation provides for a fast control of pneumatic systems and devices.
- Safety and Convenience: solenoid valves offer the ability to remotely control pneumatic mechanisms, for the safety of personnel and convenience benefits.
Apart from their use in industrial automation, solenoid valves are also employed in a range of devices that rely on pressurized air to work. Note that solenoid valves can directly control airflow, or be used indirectly to provide fore to operate a mechanism.
Resource: https://www.researchgate.net
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Types
Different types of pneumatic solenoid valves are available, with each type having been designed to suit a specific application or other need. Most often, these are categorized based on the number of ports and include 2-way, 3-way, 4-way, and 5-port valves.
2 Way
The 2-way pneumatic solenoid valve is the most basic (and common) type. It’s named so for being designed with only two ports, the inlet or upstream port and the outlet or downstream port. This valve can be a normally open or closed configuration depending on the required use. During operation, it simply shuts to isolate either port or opens to allow flow.
3 Way
This valve has 3 different ports: the inlet port that brings in a pressurized gas, the outlet port for its exit, and a third exhaust port for used air. It also has two states, open and closed. In the relaxed state, the inlet connects to the exit port. Upon closing, the outlet changes the connection to align with the exit port. This happens under the action of the solenoid, and the valve can either be a NO or NC configuration.
4 Way
The 4-way solenoid valve comes with four ports and two operating states. These consist of one inlet (also called a pressure port), two outlets, and one exhaust port. The 4-way pneumatic solenoid valve is typically a directional valve.
During operation, the action of the solenoid allows compressed air to flow through one of the outlets while also allowing each of the ports to vent used air through the exhaust.
5 Port
A 5-port pneumatic solenoid valve features a port configuration similar to that of the 4-port valve but with an exhaust port. That means an exhaust for each pressure line, unlike the 4 port valve that relies on a single exhaust for both lines.
Using two exhaust ports allows these solenoid valves to use different gas pressure levels in the two lines during operation, allowing for different actuation speeds during retraction and extension. This valve may also use two solenoids, allowing 3 other states.
Conclusion
The pneumatic solenoid valve is crucial to many air-operated mechanisms, from industrial systems to single devices. With a solenoid as its control mechanism, these valves offer several benefits, with fast action and programmable control among their biggest attributes. Solenoid-controlled valves also come in various sizes and other features, allowing users many options.

